SingSurf mathematical visualisation program
Introduction
SingSurf is program to visualise mathematical curves and surfaces. The program can calculate many of the objects found in Singularity theory and geometry:
Basic types created
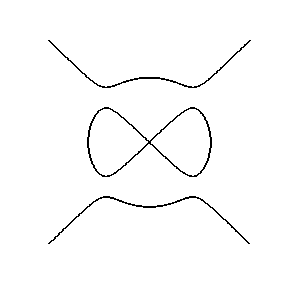
Algebraic curves defined by a single polynomial equation in two variables. e.g. electric motor
y^2(y^2-9)-x^2(x^2-10);
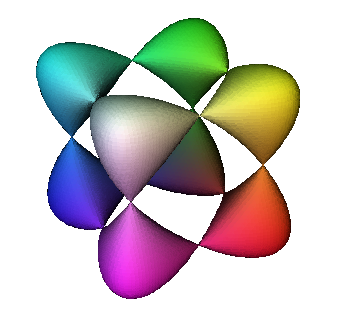
Algebraic surfaces defined by a single polynomial equation in three variables. e.g. a Chubs surface
x^4 + y^4 + z^4 - x^2 - y^2 - z^2 + 0.5;
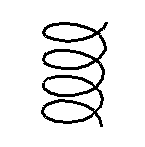
Parameterised curves defined by a 3D vector expression in a single variable. e.g. a helix
[cos(pi t), sin(pi t), t];
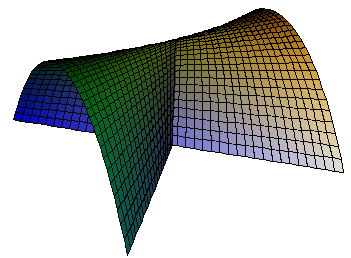
Parameterised surfaces defined by a 3D vector expression in two variables. e.g. a cross-cap
[x,x y,y^2]
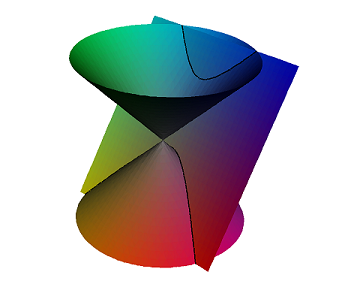
Intersection of surfaces with sets defined by another equation.
For example the intersection of a conical surface with the set defined by a plane
a x b y + cz =d.
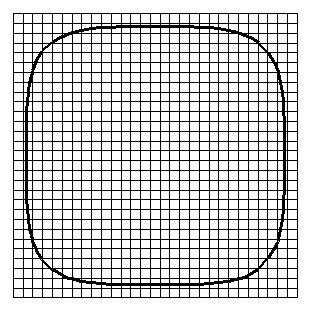
This module can be used to calculate non-polynomial curves.
For example a super ellipse
pow(abs(x/a),p)+pow(abs(y/b),p)-1
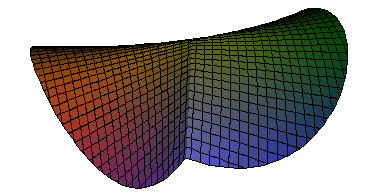
Clipping, part of a surface inside a set define by an implicit equation, like the set inside a box
min(min(min(xh-x,x-xl),min(yh-y,y-yl)),min(zh-z,z-zl)),
or clipped by a sphere
x^2+y^2+z^2-r^2
Mapping from R^3 to R^3 defined by 3D vector equation in three variables. e.g. a rotation
[cos(pi th) x - sin(pi th) y,sin(pi th) x + cos(pi th) y,z];
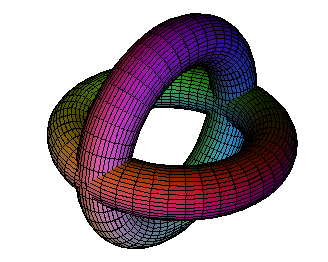
Vector Fields, including unoriented vector field, and binary differential equations
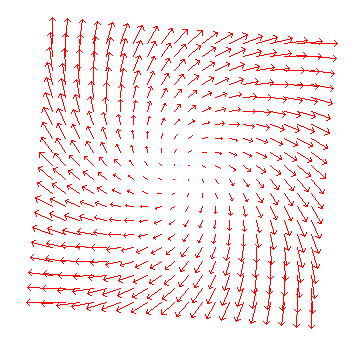
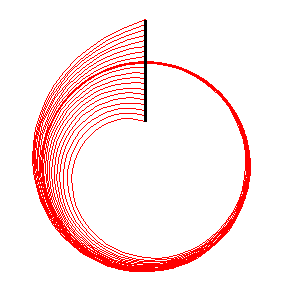
Integral Curves. Uses the points in a geometry to define the starting points
Colourise: sets the colour of a surface depending on an expression. For example to colour by the z coordinate
[(z+1), 0,(1-z)]; setting the red, green, and blue components for each point.
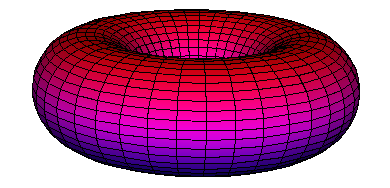
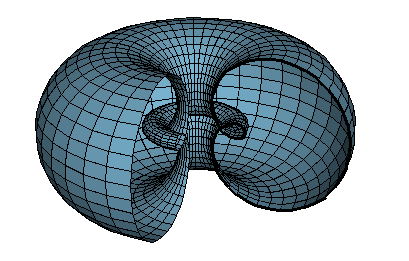
Extrude: produces surfaces of revolution and similar surfaces which depend on a curve and an equation.
Can be used to produce families of curves.
Generalised Operations
Several of these models have versions where the equation of another curve or surface can be used as part of the definition
Generalised Mappings where the equation depends on another surface. For example projection of a curve onto a surface. For example Gauss Map of a surface
N / sqrt(N.N); // Unit normal
N = Sx ^^ Sy; // calculate normal using cross product
Sx = diff(S,x); // derivatives of surface S
Sy = diff(S,y); // Definition of S read from the input surface
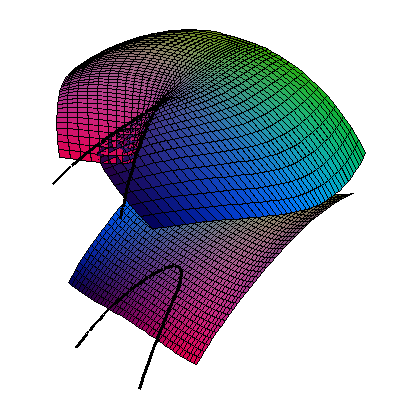
Generalised Intersections where the equation depends on the definition of another curve or surface. e.g. The profile of a surface, or parabolic lines
// The profile of a surface
N . [A,B,C];
N = diff(S,x) ^^ diff(S,y); 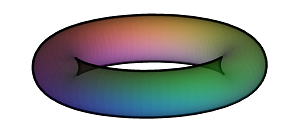
Generalised Clipping: e.g. the part of surface contained inside another already defined implicit surface
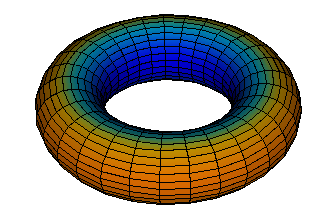
Generalised Colourise: colour by Gaussian or mean curvature
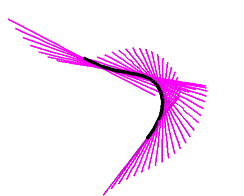
Generalised Extrude: e.g. tangent developable of a curve, or envelope of normals
S + t T; // Point on surface plus a multiple of unit tangent
T = TT/sqrt(TT.TT); // unit length
TT = diff(S,x); // tangent to curve
Generalised Vector Fields: e.g. principle directions which are calculated using the definition of the input surface
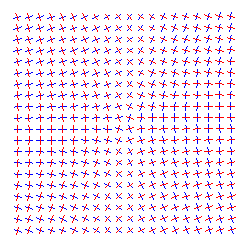
Generalised Integrals Curves: e.g. principle curves of a surface calculated using the definition of the input surface
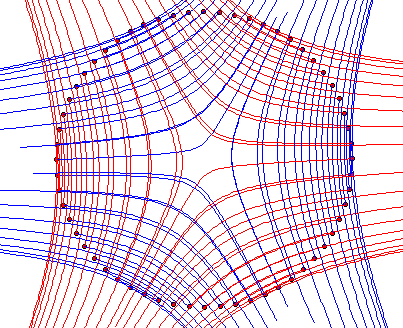
Specialised modules
Ridge Intersections: curves which depend on a surface and a vector field, for example the ridges of a surface
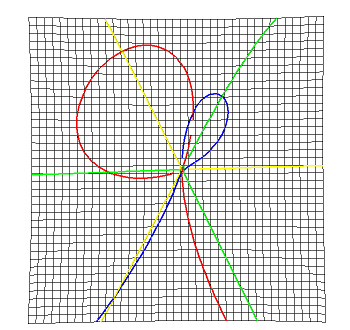
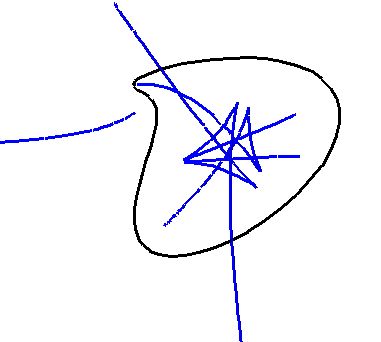
BiIntersection Intersections where the equations depends on a pair of curves. For example the pre-symmetry set of a curve.
BiMap Mapping where the equation depends on a pair of curves. For example the Symmetry set.
Projective varieties: algebraic surfaces defined in real projective space, with options for stereographic projections and rotations in 4D
Download and Installation
The program is open-source and runs on all operating systems which support Java.
See download and installation.
