Console application with calculation in different fields, structured programming constructs, matrix operations, and statistical functions.
Features include
Other feature in the package include:
This console can perform calculations using various different fields including integers, fractions, decimals with a specific number of decimal places. Use
| setfield double | for standard floating point numbers |
| setfield bigdec 30 | for big decimal numbers with 30 decimal places |
| setfield bigdec unlimited | for big decimal numbers with unlimited size |
| setfield integer | all calculations in integer |
| setfield exactint | all calculations in integers throwing exceptions on overflow |
| setfield bigint | all calculations using unlimited precision BigIntegers |
| setfield rational | for fractions (rational numbers unlimited precision) |
| setfield complex | all calculations using complex numbers |
| setfield simple | closest match to standard jep operation |
| setfield mixed 30 | combines rational numbers and bigdecimal number with 30 dp |
Notes:
The factorial(x) function can show the number of digits of precision
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
setfield integer factorial(10) factorial(20) factorial(21) factorial(22) |
Setting field INTEGER 3628800 2432902008176640000 51090942171709440000 1.1240007277776077e+21 |
Doubles work the same
setfield double factorial(21) factorial(22) |
Setting field DOUBLE 51090942171709440000 1.1240007277776077e+21 |
BigIntegers allow much larger values
setfield bigint factorial(20) factorial(30) factorial(40) factorial(50) |
Setting field BIGINT 2432902008176640000 265252859812191058636308480000000 815915283247897734345611269596115894272000000000 30414093201713378043612608166064768844377641568960512000000000000 |
Calculations with fractions
setfield rational 1/6+1/2 1/6*2/5 |
Setting field RATIONAL 2/3 1/15 |
For calculations with the complex field all results interpreted as complex numbers
setfield complex sqrt(-1) e^(i pi) format 3 e^(i pi) |
Setting field COMPLEX (0, 1) (-1, 1.2246467991473532e-16) (-1, 0) |
You can use the up down arrow keys to recal past commands.
| history | lists history, equation and values |
| showHistory [off] | to switch showing the history number on or off |
| !1 | repeat first history item |
| !2 | repeat second history item |
| !! | repeats last history item |
| !-2 | repeats last but one history item |
Special variables record the results of previous expressions
| _1, _2 | results of each first and second expression |
| __ | result of the last expression |
| m = [[1,2],[3,4]] | creation of matrix |
| u = [5,6] | creation of vector |
| m[1][2] | find element in 1st row and 2nd column |
| det(m) | the determinant of a matrix |
| trace(m) | the trace of a matrix |
| trans(m) | transpose of a matrix |
| id(3) | creates a 3x3 identity matrix |
| zeroMat(3,2) | creates a 3 by 2 matrix of zeros |
| zeroVec(3) | creates a vector of zeros length 3 |
| size(m) | finds the length of a vector or size of a matrix |
| inv(m) | find the inverse of m |
| v=solve(m,u) | find solution of m * v = u
|
| f := x^2 | set f to have and equation from the rhs |
| clean(0+1*x) | cleans an expression |
| simplify(2x+3x) | simplifies an expression using the polynomial simplification algorithm |
| expand((x+1)*(x-1)) | expands a polynomial' |
| compare((x+1)^2, x^2+2x+1) | compares with rearrangement but without expansion, returns -1,0,1 |
| symequals(x+1+x, 2x+1) | symbol equals with rearrangement but without expansion, returns true or false |
| coeffs(x^2+2x+1,x) | extract coefficients as an array |
| subst(x*y*z,y=x+1,z=x-1) | substitution rhs equations into the lhs expression |
| eval(n) | evaluate during compile time, for example: expand((x+1)^eval(n))
|
| preprocess(clean(0+x)) | cause the preprocessor to be run during evaluation. |
| eqn(f) | extract equation from a symbolic variable |
| verbose on/verbose off | switch verbose mode on or off |
Examples
| Input | Symbolic output | Numerical output |
|---|---|---|
f:=x^2 x=4 f clean(1+1 x-1) simplify(2x+3x) expand((x+1)*(x-1)) symequals(1+x+x^2+x, x^2+2x+1) compare((x+1)^2, x^2+2x+1) compare(expand((x+1)^2),expand(x^2+2x+1)) coeffs(x^2+2x+1,x) subst(x*y*z,y=x+1,z=x-1) n=3 expand((x+1)^eval(n)) coeffs(eqn(f),x) |
f:=x^2 x=4 f x 5x x^2-1 true 1 0 [1, 2, 1] x*(1+x)*(x-1) 3 1+3*x+3*x^2+x^3 [0, 0, 1] |
Cannot find value 4 16 4 20 15 true 1 0 [1, 2, 1] 60 3 125 [0, 0, 1] |
Building an equation on the fly using the eqn, eval,
and preprocess functions.
eq:=0
for(n=1;n<4;++n){preprocess(eq:=eqn(eq)+x^eval(n))}
eqn(eq)
Final result x+x^2+x^3.
| diff(x^2,x) | differentiate x^2 with respect to x |
| rules | prints the set of differentiation rules used |
Example, constructing first degree Taylor polynomial:
| Input | Symbolic output |
|---|---|
f:=sin(x)
df:=diff(f,x)
g:=subst(f,x=a)+(x-a)*subst(df,x=a)
format 3
a=0.5
for(x=0;x<=1;x+=0.1) { println(x,f,g); }
|
f:=sin(x) df:=cos(x) g:=sin(a)+(x-a)*cos(x) a=0.5 |
Final output
0.000, 0.000, -0.021 0.100, 0.100, 0.081 0.200, 0.199, 0.185 0.300, 0.296, 0.288 0.400, 0.389, 0.387 0.500, 0.479, 0.479 0.600, 0.565, 0.562 0.700, 0.644, 0.632 0.800, 0.717, 0.688 0.900, 0.783, 0.728 1.000, 0.841, 0.750
The console allows simple structured programming constructs like loops and if statements. It supports
for(i=1;i<10;++i) { ... }
while(i<10) { ... } while loops
break; (inside a loop)
continue; (inside a loop)
if(i<10) { ... } else { ... }
statement; statement
{ statement; statement }
print(a,b,c)
println(a,b,c)
e.g. A simple loop can add the numbers from 1 to 10
sum=0; for(i=1; i<=10; ++i) { sum += i; }
| x => x^2 | lambda function |
| [x,y] => x^y | lambda function with two arguments |
| apply(x=> x^2, 10) | apply function to a single item |
| map(x=> x^2, [1,2,3,4]) | apply function to every element of an array |
| fold([x,y]=> x+y, [1,2,3,4]) | sum a sequence |
| sort([x,y]=>x-y,[3,2,7,6,8]) | sort sequence according to criteria |
| filter(x=>x%2==0,[1,2,3,4,5]) | applies a filter to a list, returns the elements which meet a condition. |
| merge([x,y]=>x^y,[1,2,3,4,5],[2,2,2,2,2]) | merge two sequences element by element. |
| [1 .. 10] | short cut to define a fixed sequence |
| iterate(1,i=>i*2,i=>i<100) | generate a sequence using two lambda functions |
| define("sq",x=>x^2) | turn a lambda function into a normal function |
| sq(5) | evaluate the new function |
| Sum = seq => fold([x,y]=>x+y,seq) | Save a lambda function in a variable |
| apply(Sum,[1..10]) | Use saved lambda function |
Examples
InputSum = seq => fold([x,y]=>x+y,seq) apply(Sum,[1..10]) apply(Sum,map(x=>x^2,[1..5])) Fact = x => x<=1 ? 1 : x*apply(Fact,x-1) apply(Fact,5) Count = seq => apply(Sum,map(x=>1,seq)) apply(Count,[1..10]) E = apply(Sum,map(x=>1/apply(Fact,x),[0..20])); |
Numerical output[seq]=>fold([x,y]=>x+y,seq) 55 55 [x]=>x<=1?1:x*apply(Fact,x-1) 120 [seq]=>apply(Sum,map(x=>1,seq)) 10 2.7182818284590455 |
| count(v) | count the number of elements |
| min(v) | finds the min value in a vector or matrix |
| max(v) | finds the max value in a vector or matrix |
| sum(v) | finds the sum of the elements |
| product(v) | finds the product of the elements |
| mean(v) | finds the mean value in a vector or matrix |
| var(v) | finds the variance of the values |
| sd(v) | finds the standard deviation of the values |
| median(v) | finds the mean value in a vector or matrix |
| rank(d,data) | finds the rank of element d in data array |
| ranks(v) | finds the ranks all the elements |
| mode(v) | finds the mode of the values |
Calculation of pi using Ramanujan's formula
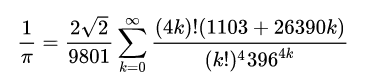
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
s=1103; a =1; c=1; d=1; \\
for(k=1;k<10;++k) {\\
a*=(4*k-3)*(4*k-2)*(4*k-1)*(4*k); \\
b =1103 + 26390*k; \\
c *= k*k*k*k; d *= 396^4; s+= a*b/(c*d); \\
v = 9801/(2*sqrt(2)*s); println(v); }
|
3.141592653589793877998905826306015 3.141592653589793238462649065702759 3.141592653589793238462643383279558 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 3.141592653589793238462643383279506 |
Calculation of e
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
s=1; f=1;
for(k=1;k<30;++k) { \\
f*=k; s+=1/f; \\
println(s); }
|
2 2.5 2.666666666666666666666666666666667 2.708333333333333333333333333333334 2.716666666666666666666666666666667 2.718055555555555555555555555555556 2.718253968253968253968253968253969 ... 2.718281828459045235360287471352545 2.718281828459045235360287471352658 |
Continued fraction for pi
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
setfield double
a=zeroVec(20);
n=pi; for(i=1;i<=20;++i) { b=floor(n); n = 1/(n-b); a[i]=b }
a
|
Setting field DOUBLE [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] 4 [3, 7, 15, 1, 292, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 14, 3, 3, 23, 1, 1, 7, 4] |
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
a=[3, 7, 15, 1, 292, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 14, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2]
for(i=1;i<=20;++i) {
s=a[i];
for(j=i-1;j>0;--j) {
s = a[j]+1/s }
println(s) }
|
[3, 7, 15, 1, 292, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 14, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2] 3 3.142857142857142857142857142857143 3.141509433962264150943396226415094 ... 3.141592653589793239014009759199591 3.141592653589793238386377506390380 3.141592653589793238493875058011561 |
f:= ...
| Input | Result |
|---|---|
f := x^2 - x - 1;
g := diff(f,x);
x=1;
for(i=0;i<5;++i) { x -= f/g; println(x,f); }
|
f:=x^2-x-1 g:=2*x-1 x=1 2, 1 1.666666666666666666666666666666667, 0.111111111111111111111111111111112 1.619047619047619047619047619047619, 0.002267573696145124716553287981859 1.618034447821681864235055724417427, 0.000001026515933067055100295739241 1.618033988749989097047296779290725, 2.10746819100131229750E-13 1.618033988749894848204586838338167, 8.882845E-27 1.618033988749894848204586834365638, 0E-33 1.618033988749894848204586834365638, 0E-33 1.618033988749894848204586834365638, 0E-33 1.618033988749894848204586834365638, 0E-33 |